Level indicators play a crucial role in various industries where precise monitoring of liquid levels is essential. From manufacturing plants to chemical facilities, understanding the different types and applications of level indicators is vital for efficient operations and safety. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of level indicators, exploring their types, working principles, and diverse applications.
Understanding Level Indicators: A Brief Overview
Level indicators are devices designed to provide real-time information about the level of liquids in tanks, vessels, or other storage containers. They ensure that operators have accurate data to manage processes, prevent overflows or shortages, and maintain a safe working environment.
Types of Level Indicators: From Traditional to Modern
1. Float Type Level Indicators:
– Working Principle: A buoyant float moves with the liquid’s level, activating a mechanical linkage connected to an indicator on the outside.
– Applications: Commonly used in large storage tanks, these indicators are cost-effective and reliable.
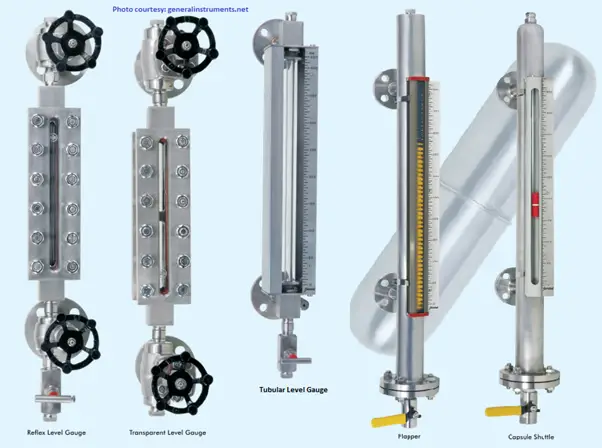
2. Sight Glass Level Indicators:
– Working Principle: Transparent glass tubes allow direct visual inspection of the liquid level. The level corresponds to the liquid height in the tube.
– Applications: Ideal for applications where direct observation is feasible, such as in laboratories or small-scale processes.
3. Ultrasonic Level Indicators:
– Working Principle: Ultrasonic waves are sent into the tank, and the time taken for the waves to return is used to determine the liquid level.
– Applications: Suitable for various industries, including water treatment, where non-contact measurement is preferred.
4. Radar Level Indicators:
– Working Principle: Radar signals are transmitted to the liquid surface, and the time taken for the signal to return is used to calculate the level.
– Applications: Commonly used in industries with challenging environmental conditions, such as oil and gas.
5. Capacitance Level Indicators:
– Working Principle: These indicators measure the change in capacitance between the probe and the tank wall as the liquid level changes.
– Applications: Suitable for both conductive and non-conductive liquids, they find use in food and pharmaceutical industries.
6. Differential Pressure Level Indicators:
– Working Principle: The difference in pressure between the liquid and the reference point is measured, providing an indirect measurement of the level.
– Applications: Widely used in pressurized vessels and chemical processing plants.
Applications of Level Indicators: From Safety to Efficiency
1. Industrial Processes:
– Level indicators are fundamental in industrial processes where precise control of liquid levels is critical. This includes chemical manufacturing, petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Water Treatment Plants:
– In water treatment facilities, level indicators ensure optimal water levels in various stages of the treatment process, preventing overflows and ensuring efficient treatment.
3. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Radar level indicators are commonly employed in the oil and gas industry to monitor levels in storage tanks and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
4. Food and Beverage Production:
– Capacitance level indicators are used in the food and beverage industry to monitor ingredients and manage production processes efficiently.
5. Environmental Monitoring:
– In environmental applications, such as monitoring water levels in reservoirs or detecting leaks in storage tanks, level indicators contribute to the overall safety and ecological health.
Choosing the Right Level Indicator: Considerations and Best Practices
1. Type of Liquid:
– Consider the nature of the liquid being measured. For corrosive substances, materials resistant to corrosion should be selected.
2. Temperature and Pressure:
– Different level indicators have varying temperature and pressure tolerances. Ensure that the selected indicator can withstand the conditions of the application.
3. Accuracy Requirements:
– The level of precision required in measurements is a critical factor. Some applications demand high accuracy, while others may tolerate a degree of variance.
4. Maintenance and Calibration:
– Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial for the accurate performance of level indicators. Choose indicators that align with the maintenance capabilities of the facility.
5. Environmental Conditions:
– Consider the environment in which the level indicator will operate. Factors like dust, humidity, and corrosive gases can impact the performance of certain types of indicators.
Level Indicators vs. Universal Joints: A Brief Comparison
Level Indicators:
1. Purpose:
– Level indicators are instruments designed to measure and display the level of liquids in tanks, vessels, or containers. They ensure accurate monitoring and control of liquid levels in industrial processes.
2. Types:
– Level indicators come in various types, including float-type indicators, sight glass indicators, ultrasonic indicators, radar indicators, and more. Each type employs different principles for level measurement.
3. Applications:
– Widely used in industries such as chemical manufacturing, water treatment, oil and gas, and food production. They play a crucial role in maintaining optimal levels for safety and efficiency.
4. Working Principle:
– The working principle varies based on the type of indicator. For example, float-type indicators use the buoyancy of a float, while ultrasonic indicators measure the time taken for ultrasonic waves to return after being sent into the liquid.
Universal Joints:
1. Purpose:
– Universal joints (also known as U-joints) are mechanical couplings that connect shafts and allow for the transmission of rotational motion between them. They are used to compensate for misalignments and transmit power.
2. Types:
– Universal joints come in several types, including single joint, double joint, and constant velocity joints (CV joints). Each type is suited for specific applications based on the required range of motion and torque transmission.
3. Applications:
– Found in various mechanical systems, including automotive drivetrains, industrial machinery, and even some steering systems. They are crucial for maintaining flexibility and compensating for misalignments in rotating shafts.
4. Working Principle:
– Universal joints consist of two yoke ends connected by a cross-shaped intermediate member. They transmit rotational motion while allowing for some degree of misalignment between the connected shafts.
Key Differences:
1. Function:
– Level indicators focus on measuring and displaying the level of liquids in containers.
– Universal joints focus on transmitting rotational motion between misaligned shafts.
2. Industry Usage:
– Level indicators are common in industries where precise liquid level control is crucial, such as manufacturing, chemicals, and water treatment.
– Universal joint is prevalent in mechanical systems like automobiles and industrial machinery.
3. Measurement vs. Motion Transmission:
– Level indicators measure the level of liquids.
– Universal joints transmit rotational motion.
4. Variety:
– Level indicators come in various types for different measurement needs.
– Universal joints have different designs for accommodating various degrees of misalignment.
In essence, level indicators are instruments for liquid level measurement, ensuring accurate and safe processes, while universal joints are mechanical couplings that facilitate the transmission of rotational motion between misaligned shafts, providing flexibility and compensating for mechanical misalignments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, level indicators are indispensable instruments in various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient management of liquids. From traditional float-type indicators to modern radar and ultrasonic technologies, the choice of a level indicator depends on the specific requirements of the application.
When selecting a level indicator, careful consideration of factors such as the type of liquid, environmental conditions, and accuracy requirements is crucial. The right choice not only ensures the reliability of measurements but also contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of industrial processes.
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation, level indicators continue to play a pivotal role, adapting to new technologies and contributing to the seamless operation of diverse processes.