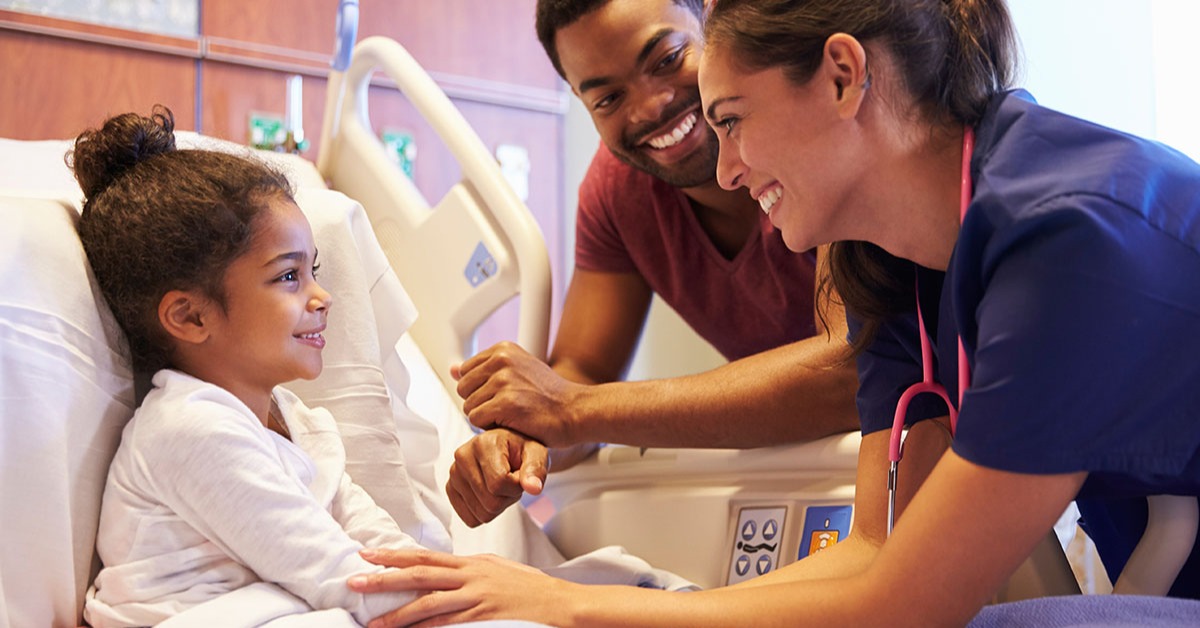
Patients are at the heart of rare disease research, playing an indispensable role in advancing medical knowledge and developing innovative treatments. Rare disease studies rely on patient involvement for insights, data, and participation that drive scientific discovery. As research continues to evolve, the contributions of patients extend beyond traditional participation, reshaping the landscape of rare disease studies and fostering a collaborative approach.
The Role of Patients in Shaping Research Priorities
Patients with rare diseases and their families have an understanding of the diseases with which they live on a daily basis that is so often unknown to researchers, and yet, the insights of patients are now sought to inform patient registries and other research efforts. Such knowledge is critical to informing research priorities. Patients frequently spot symptoms or issues that researchers might not perceive, ensuring that studies respond to concerns and needs in the real world.
Participation in Clinical Trials
Engagement of patients with rare diseases in clinical trials is critical for the success of rare disease studies. Because these conditions are relatively rare, it can be difficult to recruit enough participants. Patients’ willingness to participate in trials allows researchers to test new therapies and their efficacy.
In addition to acting traditionally as participants, patients can help in identifying potential barriers to recruitment. Travel requirements, duration of trials, and communication are among the factors that can dissuade involvement. Patients share insights that enable researchers to design trials that are more accessible, inclusive, and, consequently, improve recruitment rates and retention.
Advocating for Awareness and Funding
Patients have a powerful voice in the rare disease space for awareness and funding. Advocating for change, individuals and patient organizations raise awareness about diseases that are under-exterminated. Advocacy campaigns raise awareness, garnering more public and government support, which translates into increased investment in rare disease research.
Advocacy groups also serve as a bridge between patients and researchers. They also organize events, conferences, and educational initiatives that provide opportunities for collaboration and information sharing. Together, this collective can fast-track advances in rare disease research and ensure patient voices are heard and remain at the center of the conversation.
Providing Data Through Registries and Biobanks
Rare disease research is built from patient contributed data. The information stored in databases, registries and biobanks includes demographic data, genetic and genomic data, clinical and morbid histories, lifestyle and environmental exposures, and biospecimens. This knowledge helps scientists understand how diseases work, how to find new medications, and how to personalize treatment.
It’s crucial that patients are involved in maintaining and expanding these repositories. The inclusion of patients and their data—from those actively participating, to others aware of investigations benefiting from combing much larger databases—broadens the depths and studies available for rare disease research so that clinicians preprocessing data see less duplication of efforts. In addition, patient-driven registries frequently yield discoveries that would be impossible to make when there is little information available about a condition.
Driving Innovation Through Patient-Led Research
In recent years, patient-led research has emerged as a transformative force in rare disease studies. Patients and their families, frustrated by the slow pace of traditional research, have initiated their projects, leveraging crowdfunding, partnerships with academic institutions, and collaborations with pharmaceutical companies.
This approach empowers patients to take an active role in addressing unmet needs. By prioritizing areas overlooked by conventional research, patient-led initiatives drive innovation and pave the way for new therapies. These efforts also demonstrate the importance of patient involvement in every stage of the research process.
Building Communities and Support Networks
Because rare diseases are so infrequent, patients can often feel isolated. Establishing communities and support networks creates spaces for sharing information, personal experiences, and accessible resources. These networks provide emotional support while fostering collaboration and participation in rare disease research. Patients can also talk about their own experiences and learn about clinical research options across the world.
The Ethical Dimensions of Patient Involvement
While patient involvement is vital, it also raises ethical considerations. Ensuring informed consent, protecting patient privacy, and maintaining transparency are essential to building trust. Researchers must prioritize these principles to foster meaningful partnerships with patients.
Additionally, patients’ contributions should be recognized and valued. Acknowledging their role as co-creators of knowledge rather than passive participants promotes equity and respect in rare disease studies. This shift in perspective is critical for sustaining long-term collaboration.
Patients play a multifaceted role in rare disease research, contributing their perspectives, data, and advocacy to advance scientific discovery. Their active involvement ensures that rare disease studies remain patient-centered and impactful. By fostering collaboration between patients, researchers, and other stakeholders, the field continues to evolve, offering hope and solutions to those affected by rare diseases. As the importance of patient contributions becomes increasingly recognized, their research partnership will undoubtedly shape the future of rare disease studies.